NMRPredict Help
| Help overview | ||
| Running a Prediction | ||
| Inspecting Prediction Results | ||
| C13 NMR Prediction in Detail | ||
| Proton NMR Prediction in Detail |
Peak Search
NMRPredict contains a unique, sophisticated state of the art peak search program for searching C13 and X-nuclei databases.
First you need to load or input a peak list.
At this point you can simply hit return or click on the "Search" button to run a search. You can also modify the parameters for the line by line search in the "Line by Line Search Parameters" box at the top right hand side of the screen. The three criteria are:
- How many lines in the database spectrum must match the query peak list within the specified search deviation. The default is two less than the number of peaks in the query peak list
- The minimium number of peaks there must be in the database spectrum. The default is two less than the number of peaks in the query peak list
- The maximum number of peaks there must be in the database spectrum. The default is two more than the number of peaks in the query peak list
Below is the result of a search for peak list having 5 peaks with a tolerance of 1.5 ppm around each peak.
It should be noted that after a search you can receive up to three different hit lists:
- A SAHO hit list using the algorithm described in Organic Magnetic Resonance, Volume 15, Issue 2, Pages 178-187. This hit list can only be generated if you have supplied multiplicity information with the query peak list
- A Line By Line hit list
- A hit list containing only records which are in both the SAHO and the Line by Line hit lists
Clicking on the radio buttons next to the name of the type of hit list will load that list. All information about the database record is then displayed. You can use the forward and backward buttons to step through the hit list.
It is important to notice that the hit lists are sorted according to a hit quality index, the lower the number the better the hit. The hit quality number equates to the average difference in ppm between the query peak list and the database peak list. In the example below the hit quality is 0.39 ppm.
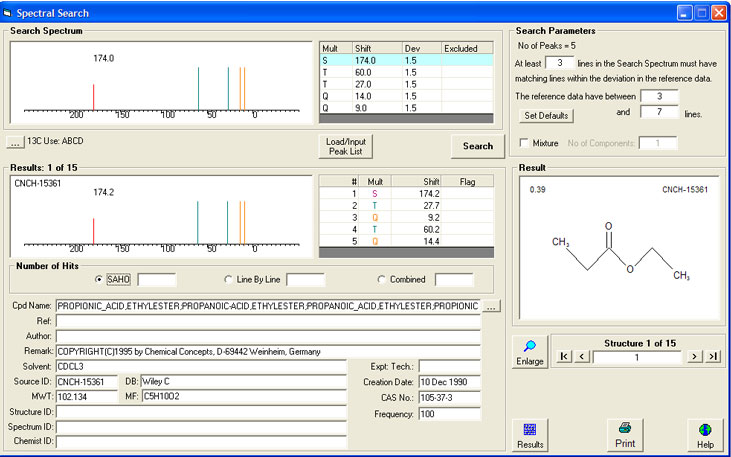
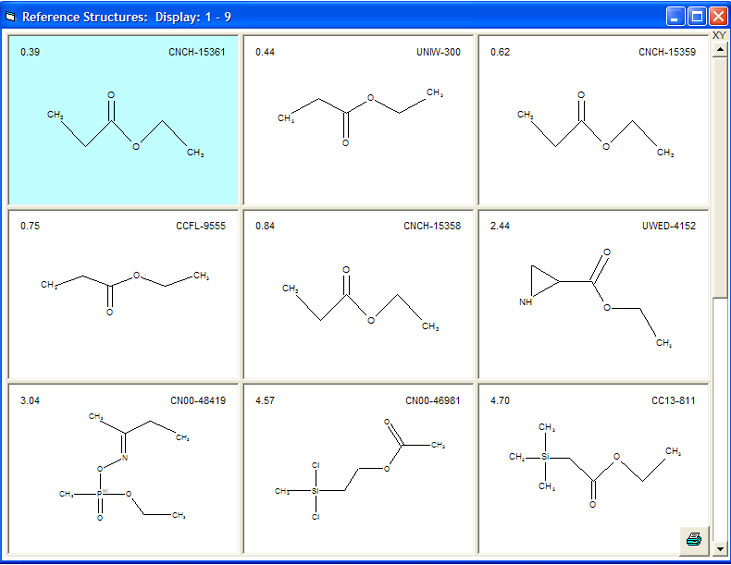
If you know your peak list contains a mixture of more than one component you can click the "Mixture" box and specify how many components you believe are present. This changes the Line by Line Search Parameters to be:
- Two less than half the number of peaks in the query peak list for many lines in the database spectrum must match the query peak list within the specified search deviation.
- Two less than half the number of peaks in the query peak list for the minimium number of peaks there must be in the database spectrum.
- Four more than half the number of peaks in the query peak list for the maximum number of peaks there must be in the database spectrum.
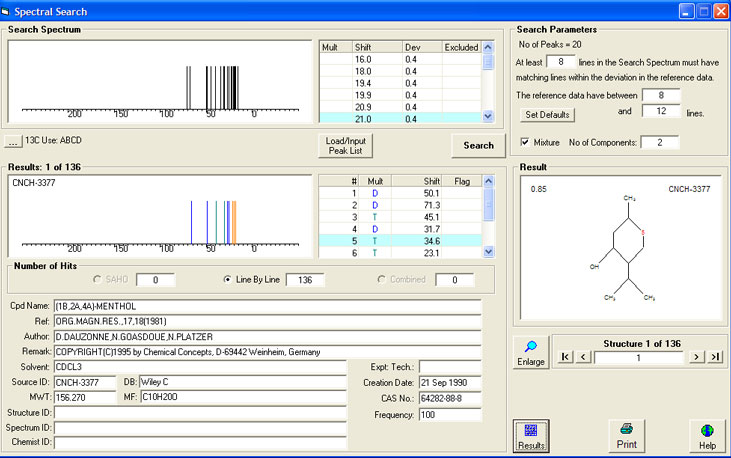
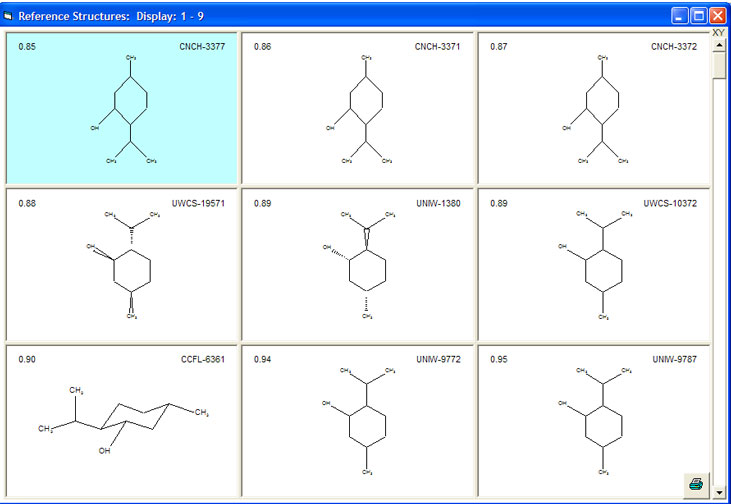
The example above, using a peak list coming from an isomeric mixture of menthols, gives the results below presented as tiled structures sorted according to the hit quality factor. From the screenshot you can clearly see how sophisticated the mixture search can be. The best ranked structures consist only of isomeric menthol derivatives.
It is highly recommended to use a deviation below 0.6 ppm when performing a mixture search.
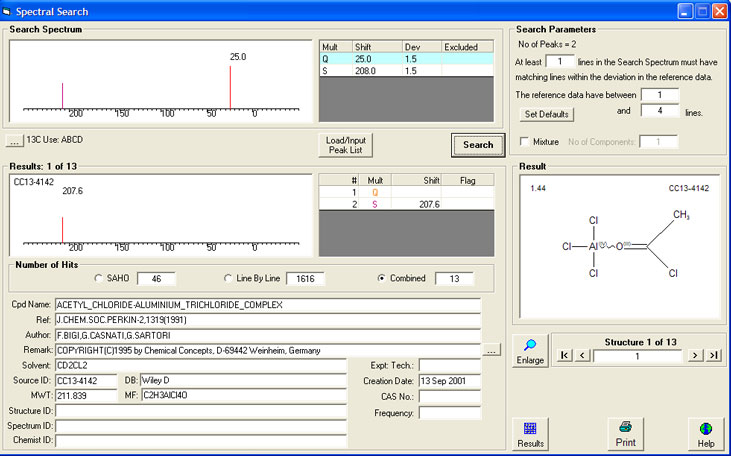
The example below shows the extreme sophistication of the implementation of the SAHO algorithm. A search for a query peak list with two peaks finds as the best match a database entry which has two peaks - but of which only one was given in the literature. The implementation of the SAHO algorithm is intelligent enough to calculate the position of the second peak during the search process. Despite this, the SAHO search is able to search a database of 263,000 records in less than 0.1 second.